Transmit and Receive - DLPS
This sample demonstrates the data transmission and reception capabilities of the CAN peripheral in DLPS mode.
Connect the USB CAN analyzer to communicate with the CAN controller via the PC by sending and receiving standard data frames, extended data frames, standard remote frames, and extended remote frames.
The SoC periodically transfers data to the PC and receives data from the PC in the CAN interrupt, then sends the same data back to the PC.
Requirements
For hardware requirements, please refer to the Requirements.
Wiring
The EVB is connected to a TJA1051 CAN Receiver module by connecting P4_0 to CTX, P4_1 to CRX. The EVB BAT/5V is connected to the module VCC and NC. The EVB GND is connected to the module GND and S.
The other end of the TJA1051 CAN Receiver module is connected to the PC via a USB CAN analyzer, by connecting module CANH to analyzer CANH and module CANL to analyzer CANL.
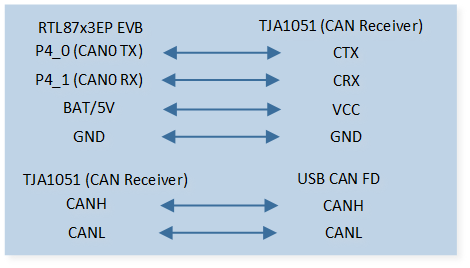
CAN TRX Demo Code Hardware Connection Diagram
The introduction of CAN transceiver can refer to CAN Transceiver Introduction .
Configurations
The following macros can be configured to enable the CAN RX FIFO function.
#define CAN_RX_FIFO_EN 0The following macros can be used to configure the period for CAN periodic transmission and reception of data.
#define CAN_TIMER_PERIOD 5000 //ms
The following macros can be configured to modify CAN pin definitions.
#define CAN_TX_PIN P4_0 #define CAN_RX_PIN P4_1
The entry function is as follows, call this function in
main()to run this sample code. For more details, please refer to the Initialization.can_trx_dlps_demo();
Building and Downloading
For building and downloading, please refer to the Building and Downloading.
Experimental Verification
Press the Reset button on the EVB and the message will be displayed in the Debug Analyzer.
can_trx_dlps_demo: start!
After IC reset, every 5 seconds, CAN will send a piece of data to the PC and wait to receive a piece of data from the PC.
Use the tool to send data frames to the IC.
On the Debug Analyzer, print the received frame data.
dlps_store: enter dlps dlps_restore: exit dlps can_trx_handler: MB_0 tx done can_basic_rx: waiting for rx... can_trx_handler: MB_7 rx done can_trx_handler: frame_type 1, frame_id = 0x100, ext_frame_id = 0x00000 can_trx_handler: rx_data [0] 0x01 ...
Code Overview
This section introduces the code and process description for initialization and corresponding function implementation in the sample.
Source Code Directory
The directory for project file and source code are as follows.
For project directory, please refer to Source Code Directory.
Source code directory:
sdk\sample\io_demo\canbus\dlps\can_trx_dlps.c.
CAN Initialization
The initialization flow for peripherals can refer to Initialization Flow.
CAN initialization flow is shown in the following figure.
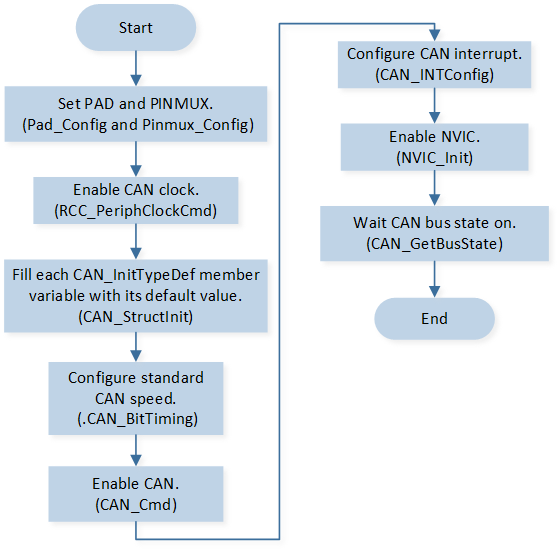
CAN Init Flow
Call
Pad_Config()andPinmux_Config()to configure the corresponding pin’s PAD and PINMUX.static void can_board_init(void) { /* Config pinmux and pad for CAN. */ Pinmux_Config(CAN_TX_PIN, CAN_TX); Pinmux_Config(CAN_RX_PIN, CAN_RX); Pad_Config(CAN_TX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(CAN_RX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); }
Call
RCC_PeriphClockCmd()to enable the CAN clock.Initialize the CAN peripheral:
Define a
CAN_InitTypeDeftypeinit_structand callCAN_StructInit()to pre-fillinit_structwith default values.Modify the
init_structparameters as needed. The CAN initialization parameters are configured as shown in the table below.Call
CAN_Init()to initialize the parameters and the CAN peripheral.
CAN Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
CAN |
|---|---|---|
Auto Re-transmit Enable |
||
CAN Speed Parameter - BRP |
3 |
|
CAN Speed Parameter - SJW |
3 |
|
CAN Speed Parameter - TSEG1 |
13 |
|
CAN Speed Parameter - TSEG2 |
4 |
Call
CAN_Cmd()to enable the corresponding CAN peripheral.Call
CAN_INTConfig()to configure the CAN receive completeCAN_RX_INTinterrupt, transmit completeCAN_TX_INTinterrupt, error interruptCAN_ERROR_INT, etc. Configure NVIC, and refer to Interrupt Configuration for NVIC-related configurations.Call
CAN_GetBusState()to loop-check the CAN bus state and wait for the CAN bus to open.while (CAN_GetBusState(CAN0) != CAN_BUS_STATE_ON) { __asm volatile ( "nop \n" ); }
Note
If the program is stuck at the point of waiting for the CAN bus to be on, please check if the CAN bus is connected correctly.
DLPS Mode Initialization
Call
os_timer_create()to create a timer with a periodic interval.Call
os_timer_start()to start timer.Call
io_dlps_register()to initialize IO store/restore and do not need to worry about which IO peripheral requires specific handling.Call
power_check_cb_register()to register inquiry callback function to DLPS Framework. This function will be called each time before entering DLPS to decide whether DLPS is allowed to enter. DLPS will be disallowed if any inquiry callback function returns false. Functioncan_dlps_check_callbackwill be executed before entering DLPS.Call
io_dlps_register_enter_cb()to register callbacks to DLPS enter stage. Functiondlps_storewill be executed while entering DLPS.Call
Pad_Config()to configCAN_TX_PINandCAN_RX_PINpull up in order to prevent leakage.
Call
io_dlps_register_exit_cb()to register callbacks to DLPS exit stage. Functiondlps_restorewill be executed while exiting from DLPS.Call
Pad_Config()to configCAN_TX_PINandCAN_RX_PINpull none.
Call
bt_power_mode_set()to set Bluetooth MAC deep sleep mode.Call
power_mode_set()to switch the system to DLPS mode.
Functional Implementation
When the timer expires, the SoC will wake up from DLPS, send a piece of data to the PC, and wait to receive data from the PC.
The
can_timer_handlerwill be called when the timer expires.Call
can_basic_txto send a standard data frame.Configure the message buffer to TX mode using the set transmit frame type.
Enable the message buffer TX interrupt. Poll the RAM status to be idle.
Call
can_dlps_disableto disable DLPS and wait for the CAN TX to complete.
void can_basic_tx(uint32_t buf_id, uint8_t frame_type, \ uint16_t frame_id, uint32_t ext_id, uint8_t *tx_data, uint8_t data_len) { CANError_TypeDef tx_error; CANTxFrame_TypeDef tx_frame_type; tx_frame_type.msg_buf_id = buf_id; tx_frame_type.frame_type = frame_type; tx_frame_type.standard_frame_id = frame_id; tx_frame_type.auto_reply_bit = DISABLE; tx_frame_type.extend_frame_id = 0; switch (frame_type) { ... } CAN_MBTxINTConfig(CAN0, tx_frame_type.msg_buf_id, ENABLE); tx_error = CAN_SetMsgBufTxMode(CAN0, &tx_frame_type, tx_data, data_len); ... can_dlps_disable(APP_DLPS_ENTER_CHECK_CAN_TX(buf_id)); }
Call
can_basic_rxto wait for the PC to send a frame.Use message buffer 12 to receive frame if FIFO mode is enabled.
Mask the rtr, ide, and id bit filters to receive all frames.
Disable RX GDMA. Disable auto reply.
Configure the message buffer to RX mode using the set receive frame type.
Enable the message buffer RX interrupt. Poll the RAM status to be idle.
Call
can_dlps_disableto disable DLPS and wait for the PC to send data.
void can_basic_rx(void) { CANError_TypeDef rx_error; CANRxFrame_TypeDef rx_frame_type; rx_frame_type.msg_buf_id = buf_id; rx_frame_type.extend_frame_id = 0; rx_frame_type.standard_frame_id = 0; rx_frame_type.frame_rtr_mask = CAN_RX_FRAME_MASK_RTR; rx_frame_type.frame_ide_mask = CAN_RX_FRAME_MASK_IDE; rx_frame_type.frame_id_mask = CAN_RX_FRAME_MASK_ID; rx_frame_type.rx_dma_en = RESET; rx_frame_type.auto_reply_bit = RESET; rx_error = CAN_SetMsgBufRxMode(CAN0, &rx_frame_type); CAN_MBRxINTConfig(CAN0, rx_frame_type.msg_buf_id, ENABLE); ... can_dlps_disable(APP_DLPS_ENTER_CHECK_CAN_RX(buf_id)); }
After the data transmission is complete, it will enter the interrupt
can_trx_handler.Call
CAN_ClearINTPendingBit()to clear TX interrupt.Call
CAN_ClearMBnTxDoneFlag()to clear message buffer TX done flag.Call
can_dlps_enableto enable DLPS.
CAN_ClearINTPendingBit(CAN0, CAN_TX_INT_FLAG); for (uint8_t index = 0; index < CAN_MESSAGE_BUFFER_MAX_CNT; index++) { if (SET == CAN_GetMBnTxDoneFlag(CAN0, index)) { IO_PRINT_INFO1("can_trx_handler: MB_%d tx done", index); CAN_ClearMBnTxDoneFlag(CAN0, index); /* Add user code. */ can_dlps_enable(APP_DLPS_ENTER_CHECK_CAN_TX(index)); } }
When data is received, it will enter the interrupt
can_trx_handler.Read and print the received frame data sequentially from the message buffer that generated the receive completion interrupt.
Call
CAN_ClearINTPendingBit()to clear RX interrupt.Call
CAN_ClearMBnRxDoneFlag()to clear message buffer RX done flag.Call
can_dlps_enableto enable DLPS.
CAN_ClearINTPendingBit(CAN0, CAN_RX_INT_FLAG); ... CAN_ClearMBnRxDoneFlag(CAN0, index); CANMsgBufInfo_TypeDef mb_info; CAN_GetMsgBufInfo(CAN0, index, &mb_info); ... CAN_GetRamData(CAN0, mb_info.data_length, rx_data); CANDataFrameSel_TypeDef frame_type = CAN_CheckFrameType(mb_info.rtr_bit, mb_info.ide_bit, mb_info.edl_bit); ... /* Send back frame here. */ can_basic_tx(0, frame_type, mb_info.standard_frame_id, \ mb_info.extend_frame_id, rx_data, mb_info.data_length); can_dlps_enable(APP_DLPS_ENTER_CHECK_CAN_RX(index)); ...