SPI Master High Speed
This sample demonstrates how SPI0 sends and receives data in high-speed mode. In this example, SPI is configured as a master and the direction is full-duplex. The SPI clock is set to 40MHz, and it is recommended to use DMA mode and dedicated pins for high speed. The chip writes some data to SPI slave and then chip reads data from SPI slave.
Requirements
For hardware requirements, please refer to the Requirements.
Wiring
Connect P1_2 (master CS) to CS of SPI slave device, connect P1_3 (master SCK) to SCK of SPI slave device, connect P1_4 (master MOSI) to MOSI of SPI slave device, and connect P1_5 (master MISO) to MISO of SPI slave device.
The hardware connection of SPI sample code is shown in the figure below.
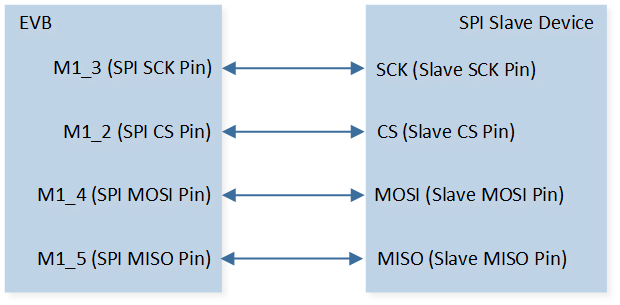
SPI Sample Code Hardware Connection Diagram
Configurations
The following macros can be configured to modify pin definitions.
#define SPI0_HS_CS P1_2#define SPI0_HS_SCK P1_3#define SPI0_HS_MOSI P1_4#define SPI0_HS_MISO P1_5
The entry function is as follows, call this function in
main()to run this sample code. For more details, please refer to the Initialization.spi0_hs_dma_demo();
Building and Downloading
For building and downloading, please refer to the Building and Downloading.
Experimental Verification
Press the Reset button on the EVB, the data in the array
sendbufis sent to SPI slave device.When completing the transmission, it enters the GDMA interrupt and prints log.
spi_tx_dma_handlerAfter the slave device receives the data, the slave device sends data to the chip. The chip stores the received data in array
readbufand prints the received data in Debug Analyzer.spi_rx_dma_handler: readbuf[0] 0x%x ... spi_rx_dma_handler: readbuf[1023] 0x%x
Code Overview
Source Code Directory
For project directory, please refer to Source Code Directory.
Source code directory:
sdk\src\sample\io_demo\spi\spi0_hs\spi0_hs_dma_demo.c.
SPI Initialization Flow
The initialization flow for peripherals can refer to Initialization Flow.
SPI initialization flow is shown in the following figure.
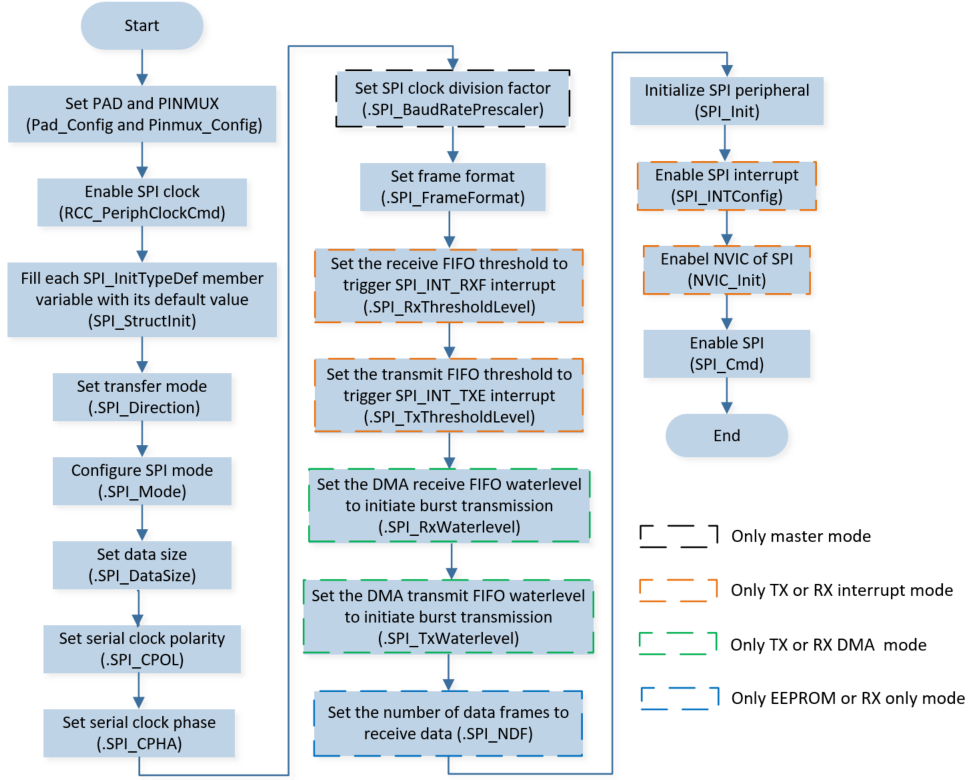
SPI Initialization Flow Chart
Call
Pad_Config()andPinmux_Config()to initialize the pin.static void board_spi_init(void) { /* SPI0 */ Pinmux_Config(SPI0_HS_SCK, SPI0_CLK_MASTER); Pinmux_Config(SPI0_HS_MOSI, SPI0_MO_MASTER); Pinmux_Config(SPI0_HS_MISO, SPI0_MI_MASTER); Pinmux_Config(SPI0_HS_CS, SPI0_SS_N_0_MASTER); Pad_Config(SPI0_HS_SCK, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(SPI0_HS_MOSI, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(SPI0_HS_MISO, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(SPI0_HS_CS, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); }
Call
pm_cpu_freq_set()to set CPU frequency to 120MHz.Call
pll4_enable_cko1to enable PLL4 clock, and callRCC_SPIClkSourceSwitch()to switch PLL4 as SPI0 clock source.Call
RCC_PeriphClockCmd()to enable the SPI clock and function.Initialize the SPI peripheral:
Define the
SPI_InitTypeDeftypeSPI_InitStructure, and callSPI_StructInit()to pre-fillSPI_InitStructurewith default values.Modify the
SPI_InitStructureparameters as needed. The SPI initialization parameter configuration is shown in the table below.Call
SPI_Init()to initialize the SPI peripheral,SPI0_HSis seleted.
SPI Initialization Parameters SPI Hardware Parameters
Setting in the
SPI_InitStructureSPI
Direction
Device Role (SPI Master or SPI Slave)
Data Frame Size
Clock Polarity
Clock Phase
Clock Div
4
Receive FIFO Threshold Level
0
Frame Format
RX Sample Delay
1
TX Water Level
25
RX Water Level
31
TX DMA Initialization Flow
The initialization flow for peripherals can refer to Initialization Flow.
SPI TX DMA initialization flow is shown in the following figure.
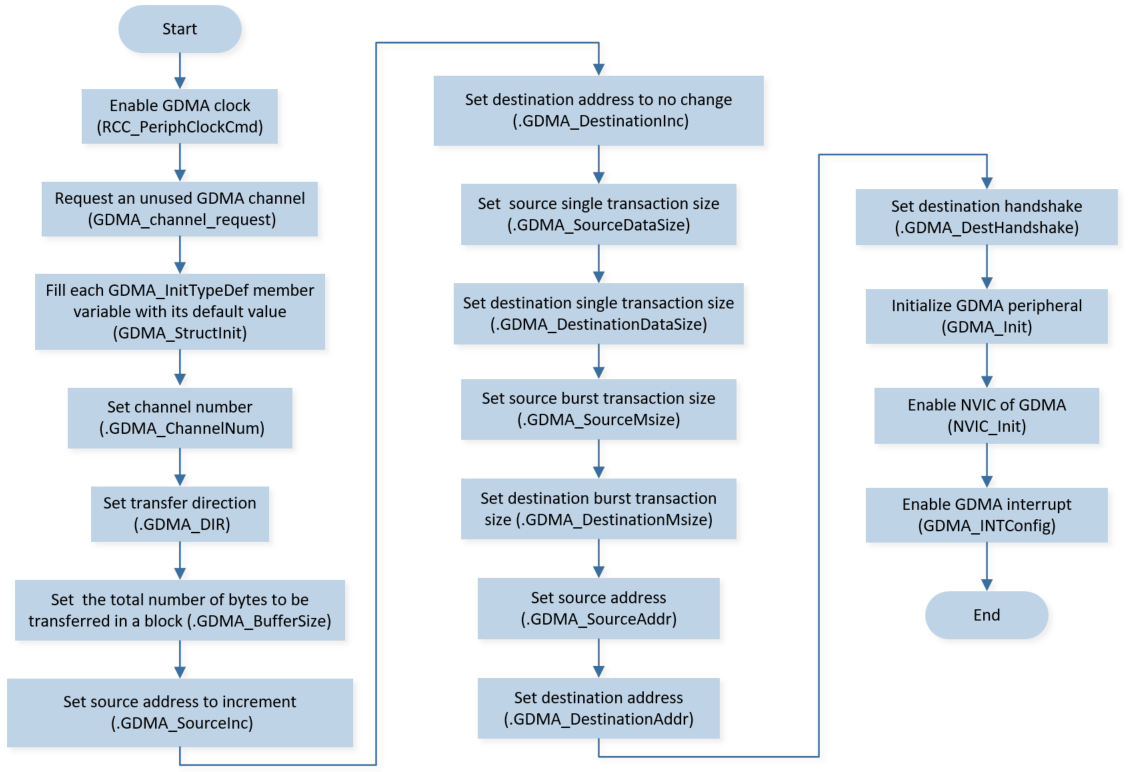
SPI TX DMA Initialization Flow Chart
Call
RCC_PeriphClockCmd()to enable the GDMA clock and function.Initialize the GDMA peripheral:
Define the
GDMA_InitTypeDeftypeGDMA_InitStruct, and callGDMA_StructInit()to pre-fillGDMA_InitStructwith default values.Modify the
GDMA_InitStructparameters as needed. The GDMA initialization parameter configuration is shown in the table below.Call
GDMA_Init()to initialize the GDMA peripheral.
GDMA Initialization Parameters GDMA Hardware Parameters
Setting in the
GDMA_InitStructGDMA
Channel Num
SPI_TX_DMA_CHANNEL_NUMTransfer Direction
Buffer Size
DMA_BUFFER_SIZESource Address Increment or Decrement
Destination Address Increment or Decrement
Source Data Size
Destination Data Size
Source Burst Transaction Length
Destination Burst Transaction Length
Source Address
sendbufDestination Address
SPI0_HS->DRDestination Handshake
GDMA_Handshake_SPI0_TXCall
RamVectorTableUpdate()to register the TX GDMA interrupt handler.Call
GDMA_INTConfig()to enable TX GDMA transfer complete interruptGDMA_INT_Transfer.Call
NVIC_Init()to enable NVIC of TX GDMA.
RX DMA Initialization Flow
The initialization flow for peripherals can refer to Initialization Flow.
SPI RX DMA initialization flow is shown in the following figure.
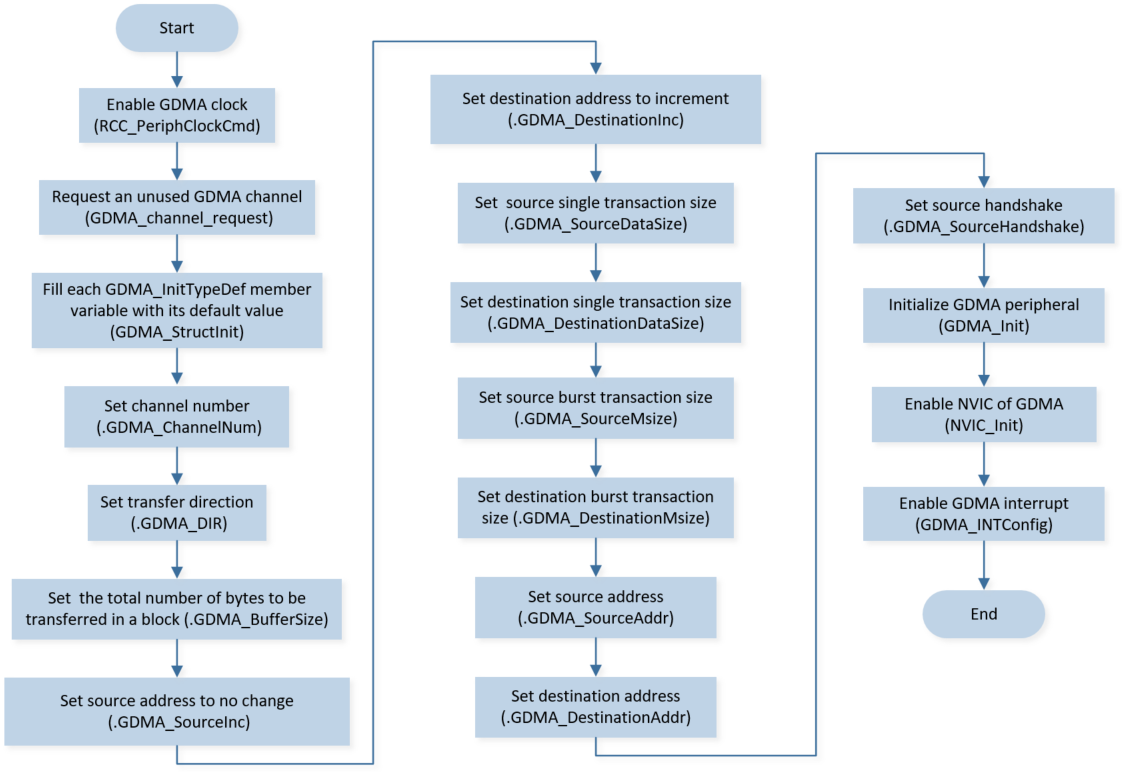
SPI RX DMA Initialization Flow Chart
Initialize the GDMA peripheral:
Define the
GDMA_InitTypeDeftypeGDMA_InitStruct, and callGDMA_StructInit()to pre-fillGDMA_InitStructwith default values.Modify the
GDMA_InitStructparameters as needed. The GDMA initialization parameter configuration is shown in the table below.Call
GDMA_Init()to initialize the GDMA peripheral.
GDMA Initialization Parameters GDMA Hardware Parameters
Setting in the
GDMA_InitStructGDMA
Channel Num
SPI_RX_DMA_CHANNEL_NUMTransfer Direction
Buffer Size
DMA_BUFFER_SIZESource Address Increment or Decrement
Destination Address Increment or Decrement
Source Data Size
Destination Data Size
Source Burst Transaction Length
Destination Burst Transaction Length
Source Address
SPI0_HS->DRDestination Address
readbufSource Handshake
GDMA_Handshake_SPI0_RXCall
RamVectorTableUpdate()to register the RX GDMA interrupt handler.Call
GDMA_INTConfig()to enable RX GDMA transfer complete interruptGDMA_INT_Transfer.Call
NVIC_Init()to enable NVIC of RX GDMA.
Functional Implementation
Master Receive Data by DMA
Call
SPI_GDMACmd()to disable and then enable SPI GDMA RX Function.Call
GDMA_Cmd()to enable RX DMA transfers.When GDMA transfer is completed, transfer complete interrupt is triggered. Then call
GDMA_ClearINTPendingBit()to clearGDMA_INT_Transferinterrupt.
Master Send Data by DMA
Call
SPI_GDMACmd()to disable and then enable SPI GDMA TX Function.Call
GDMA_Cmd()to enable TX DMA transfers.When GDMA transfer is completed, transfer complete interrupt is triggered. Then call
GDMA_ClearINTPendingBit()to clearGDMA_INT_Transferinterrupt.