Transmit And Receive - GDMA
This sample demonstrates the functionality of sending and receiving data via CAN using GDMA.
The CAN controller is connected to a USB CAN analyser and communicates with the CAN controller by sending and receiving standard data frames, extended data frames, standard remote frames, extended remote frames and other frame types through the PC side.
The chip side receives the data from the PC via GDMA and transmits the same data to the PC side via GDMA and the PC side receives the data back from the chip.
Requirements
For requirements, please refer to the Requirements.
Wiring
The EVB is connected to a TJA1051 CAN Receiver module by connecting P3_2 to CTX, P3_4 to CRX. The EVB VCC3.3V is connected to the module VCC. The EVB GND is connected to the module GND.
The other end of the TJA1051 CAN Receiver module is connected to the PC via a USB CAN analyzer, by connecting module CANH to analyzer CANH and module CANL to analyzer CANL.
The hardware connection diagram is as follows:
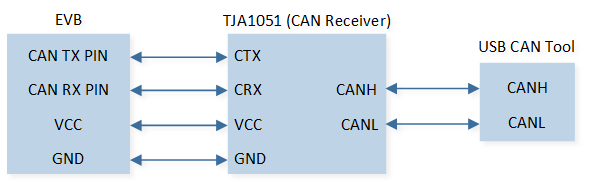
CAN Hardware Connection Diagram
The introduction of CAN transceiver can refer to CAN Transceiver Introduction.
Building and Downloading
For building and downloading, please refer to the Building and Downloading.
Experimental Verification
After the IC is reset, a data frame sent by the IC is received on the tool.
-
The IC prints the log waiting to be received:
[CAN] start can trx_gdma demo! [CAN] BUS state: 0, waiting... [CAN] BUS ON 1 [TX DMA HANDLER] TX DONE! [CAN] waiting for rx...
Send a data frame using the tool.
-
The IC receives the data frame via GDMA and prints log.
[CAN HANDLER] CAN RX [CAN HANDLER] MB_1 rx done [RX DMA HANDLER] GDMA_Channel_Handler [RX DMA HANDLER] std id = 0x00000100, ext id = 0x00000000 dlc = 8 [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [0] 0x01 [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [1] 0x23 [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [2] 0x45 [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [3] 0x67 [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [4] 0x89 [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [5] 0xab [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [6] 0xcd [RX DMA HANDLER] rx_data [7] 0xef [CAN] waiting for rx...
Code Overview
This section introduces the code and process description for initialization and corresponding function implementation in the sample.
Source Code Directory
The directory for project file and source code are as follows:
Project directory:
sdk\samples\peripheral\adc\continuous_gdma\projSource code directory:
sdk\samples\peripheral\adc\continuous_gdma\src
Initialization
The initialization flow for peripherals can refer to Initialization Flow in General Introduction.
-
Call
Pad_Config()andPinmux_Config()to configure the corresponding pin's PAD and PINMUX.void can_board_init(void) { /* Config pinmux and pad for CAN. */ Pinmux_Config(CAN_TX_PIN, CAN_TX); Pinmux_Config(CAN_RX_PIN, CAN_RX); Pad_Config(CAN_TX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(CAN_RX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); }
Call
RCC_PeriphClockCmd()to enable the CAN clock.-
Initialize the CAN peripheral:
Define a
CAN_InitTypeDeftypeinit_structand callCAN_StructInit()to pre-fillinit_structwith default values.Modify the
init_structparameters as needed. The CAN initialization parameters are configured as shown in the table below.Call
CAN_Init()to initialize the parameters and the CAN peripheral.
CAN Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
CAN |
|---|---|---|
Auto Re-transmit Enable |
||
CAN speed parameter - brp |
3 |
|
CAN speed parameter - sjw |
3 |
|
CAN speed parameter - tseg1 |
13 |
|
CAN speed parameter - tseg2 |
4 |
|
Rx GDMA Enable |
Call
CAN_Cmd()to enable the corresponding CAN peripheral.Call
CAN_INTConfig()to configure the CAN receive completeCAN_RX_INTinterrupt, transmit completeCAN_TX_INTinterrupt, error interruptCAN_ERROR_INT, etc. Configure NVIC, and refer to Interrupt Configuration for NVIC-related configurations.-
Call
CAN_GetBusState()to loop-check the CAN bus state and wait for the CAN bus to open.while (CAN_GetBusState() != CAN_BUS_STATE_ON) { __asm volatile ( "nop \n" ); }
Note
If the program is stuck at the point of waiting for the CAN bus to be on, please check if the CAN bus is connected correctly.
Call
RCC_PeriphClockCmd()to enable the GDMA clock.-
Initialize the GDMA peripheral:
Define a
GDMA_InitTypeDeftypeGDMA_InitStructand executeGDMA_StructInit()to pre-fillGDMA_InitStructwith default values.Modify the
GDMA_InitStructparameters as needed. The initialization parameter configuration for GDMA TX and RX channels is shown in the following table. ExecuteGDMA_Init()to initialize the GDMA peripheral.Configure the GDMA total transfer complete interrupt
GDMA_INT_Transferand NVIC. Refer to Interrupt Configuration for related NVIC configurations.
GDMA Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
GDMA TX Channel |
GDMA RX Channel |
|---|---|---|---|
Channel Num |
1 |
0 |
|
Transfer Direction |
|||
Buffer Size |
|
- |
|
Source Address Increment or Decrement |
|||
Destination Address Increment or Decrement |
|||
Source Data Size |
|||
Destination Data Size |
|||
Source Burst Transaction Length |
|||
Destination Burst Transaction Length |
|||
Source Address |
- |
|
|
Destination Address |
|
- |
|
Source Handshake |
- |
||
Destination Handshake |
- |
- |
Note
During the initialization of the GDMA peripheral, do not initialize the source address of the TX GDMA channel and the destination address of the RX GDMA channel; these will be adjusted dynamically later.
Functional Implementation
Call the
can_dma_txfunction to configure the valuetx_can_ram_structthat needs to be set in the RAM register via TX GDMA.-
Call the
can_start_tx_dmafunction.Set the source address of the TX GDMA channel to the address of
tx_can_ram_struct.Enable the
GDMA_INT_Transferinterrupt for TX GDMA.Enable the GDMA peripheral to start the transmission.
void can_start_tx_dma(CAN_RAM_TypeDef *p_can_ram_data) { GDMA_SetSourceAddress(TX_GDMA_Channel, (uint32_t)p_can_ram_data); GDMA_INTConfig(TX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer, ENABLE); GDMA_Cmd(TX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, ENABLE); }
-
After enabling the GDMA TX channel, GDMA transfers data from
tx_can_ram_structto(CAN->CAN_RAM_DATA). When TX is completed, a GDMA TX interrupt is triggered, and relevant information is printed.GDMA_INTConfig(TX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer, DISABLE); DBG_DIRECT("[TX GDMA HANDLER] TX DONE!"); GDMA_ClearINTPendingBit(TX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer);
-
Call the
can_dma_rxfunction.Mask the reception of frames rtr, ide, and id filtering, i.e., receive all frames.
Enable Rx GDMA and disable automatic reply.
Configure the message buffer to receive mode using the set reception frame type.
Enable message buffer reception interrupt and wait for the RAM status to be idle.
... rx_frame_type.msg_buf_id = RX_DMA_BUF_ID; rx_frame_type.frame_rtr_mask = SET; rx_frame_type.frame_ide_mask = SET; rx_frame_type.frame_id_mask = CAN_FRAME_ID_MASK_MAX_VALUE; rx_frame_type.rx_dma_en = SET; rx_frame_type.auto_reply_bit = RESET; rx_error = CAN_SetMsgBufRxMode(&rx_frame_type); CAN_MBRxINTConfig(rx_frame_type.msg_buf_id, ENABLE); while (CAN_GetRamState() != CAN_RAM_STATE_IDLE) ...
-
When the message buffer reception is complete, execute the interrupt handler function
CAN_Handler.Call the
CAN_GetRxDmaMsize()function to obtain the Rx GDMA buffer size.Call the
can_start_rx_dmafunction to enable the configuration of the GDMA buffer size, configure the destination address of the GDMA RX channel, and enable RX GDMA transmission.
if (dma_en_flag == ENABLE) { uint32_t dma_buffer_size = CAN_GetRxDmaMsize(); can_start_rx_dma((uint32_t)&rx_dma_data_struct, dma_buffer_size); } ... GDMA_SetBufferSize(RX_GDMA_Channel, buffer_size); GDMA_SetDestinationAddress(RX_GDMA_Channel, des_addr); GDMA_INTConfig(RX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer, ENABLE); GDMA_Cmd(RX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, ENABLE);
-
After enabling the GDMA RX channel, when CAN receives data, the GDMA transfers the data from
&(CAN->CAN_RX_DMA_DATA)torx_dma_data_struct. When the RX GDMA reception is complete, the interrupt handler functionRX_GDMA_Channel_Handleris executed.Disable the
GDMA_INT_Transferinterrupt for RX GDMA.Enable the RX GDMA of the message buffer to start the next reception.
Print the received frame ID and print the received frame data.
Clear the
GDMA_INT_Transferinterrupt flag for RX GDMA.
GDMA_INTConfig(RX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer, DISABLE); ... CAN_SetMBnRxDmaEnFlag(RX_DMA_BUF_ID, ENABLE); ... DBG_DIRECT(...); ... GDMA_ClearINTPendingBit(RX_GDMA_CHANNEL_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer);
See Also
Please refer to the relevant API Reference: