Analog Microphone
This example code collects AMIC data and encodes it into PCM voice data using the CODEC.
AMIC collects analog voice data, which is encoded by CODEC and sent to the I2S receive FIFO. The data is then transferred to UART using GDMA.
On the PC side, a serial assistant receives the data transmitted by UART. Audio parsing software is used to analyze the data and play the recorded voice. In this example, the audio parsing software used is Audacity.
Requirements
For requirements, please refer to the Requirements.
In addition, you need to install PuTTY or UartAssist serial assistant tools and audio parsing tools like Audacity on the PC terminal.
Wiring
Connect the AMIC module to the EVB, connect MICBIAS to 1.8V, GND to GND, MIC_P to P2_6, and MIC_N to P2_7;
Connect the FT232 module to the EVB to receive UART data, connecting P3_2 to RXD, and P3_3 to TXD.
Building and Downloading
For building and downloading, please refer to the Building and Downloading.
Experimental Verification
Preparation Stage
Start the PC terminal with PuTTY or UartAssist, use ASCII to receive data, open the UART COM port, and make the following UART settings:
Baud rate: 3000000
8 data bits
1 stop bit
No parity
No hardware flow control
Set the output data bytes to redirect to a file.
Start the audio parsing software and select the parsing format according to the settings in CODEC. In this example, you can refer to the following Audacity settings.
Encoding: 16-bit PCM
Endianness: Little Endian
Channels: 1 channel
Sample rate: 1600 Hz
Testing Stage
From start to finish of recording, the collected voice data is encoded by CODEC as PCM data and sent to the PC terminal via UART.
Use the audio parsing software to view the decoded voice waveform and play the voice.
Code Overview
This section introduces the code and process description for initialization and corresponding function implementation in the sample.
Source Code Directory
The directory for project file and source code are as follows:
Project directory:
sdk\samples\peripheral\codec\amic\projSource code directory:
sdk\samples\peripheral\codec\amic\src
Initialization
The initialization flow for peripherals can refer to Initialization Flow in General Introduction.
The initialization process includes initializing the CODEC / UART / I2S / GDMA modules as follows.
-
Call
Pad_Config()andPinmux_Config()to configure the PAD and PINMUX of the corresponding pins. The I2S pin multiplexing functions are BCLK_SPORT0, LRC_RX_SPORT0, SDI_CODEC_SLAVE, and SDO_CODEC_SLAVE.void board_codec_init(void) { Pad_Config(AMIC_MSBC_CLK_PIN, PAD_SW_MODE, PAD_NOT_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE,PAD_OUT_HIGH); Pad_Config(AMIC_MSBC_DAT_PIN, PAD_SW_MODE, PAD_NOT_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_DISABLE,PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(CODEC_BCLK_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_ENABLE,PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(CODEC_LRCLK_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_ENABLE,PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(CODEC_TX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_ENABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pad_Config(CODEC_RX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_NONE, PAD_OUT_ENABLE, PAD_OUT_LOW); Pinmux_Config(CODEC_BCLK_PIN, BCLK_SPORT0); Pinmux_Config(CODEC_LRCLK_PIN, LRC_RX_SPORT0); Pinmux_Config(CODEC_TX_PIN, SDI_CODEC_SLAVE); Pinmux_Config(CODEC_RX_PIN, SDO_CODEC_SLAVE); }
-
Call
Pad_Config()andPinmux_Config()to configure the PAD and PINMUX for the UART module corresponding pins.void board_uart_init (void) { Pad_Config(UART_TX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_UP, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_HIGH); Pad_Config(UART_RX_PIN, PAD_PINMUX_MODE, PAD_IS_PWRON, PAD_PULL_UP, PAD_OUT_DISABLE, PAD_OUT_HIGH); Pinmux_Config(UART_TX_PIN, UART5_TX); Pinmux_Config(UART_RX_PIN, UART5_RX); }
Execute
I2S_StructInit()andI2S_Init()to initialize the I2S peripheral. Configuration parameters for the I2S0 initialization are as follows:
I2S Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
I2S master RX |
|---|---|---|
Sample Rate (Mi) |
0x271 |
|
Sample Rate (Ni) |
0x10 |
|
Device Mode |
||
Channel Type |
||
Data Format |
||
Data Width |
Execute
UART_StructInit()andUART_Init()to initialize the UART peripheral. Configuration parameters for the UART initialization are as follows:
UART Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
UART |
|---|---|---|
UART Div |
1 |
|
UART Ovsr |
8 |
|
UART OvsrAdj |
0x492 |
|
UART Tx Dma En |
||
UART Dma En |
Execute
GDMA_StructInit()andGDMA_Init()to initialize the GDMA peripheral. Configuration parameters for the GDMA initialization are as follows:
GDMA Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
GDMA Channel |
|---|---|---|
Channel Num |
0 |
|
Transfer Direction |
||
Buffer Size |
1000 |
|
Source Address Increment or Decrement |
||
Destination Address Increment or Decrement |
||
Source Data Size |
||
Destination Data Size |
||
Source Burst Transaction Length |
||
Destination Burst Transaction Length |
||
Source Address |
|
|
Destination Address |
|
|
Source Handshake |
||
Destination Handshake |
Configure the GDMA transfer complete interrupt
GDMA_INT_Transferand NVIC. Related NVIC configuration can be referred to in Interrupt Configuration.-
Initialize the CODEC peripheral.
Call
CODEC_AnalogCircuitInit()to initialize the analog circuit.Call
RCC_PeriphClockCmd()to enable the CODEC clock.Execute
CODEC_StructInit()andCODEC_Init()to initialize the CODEC peripheral. Configuration parameters for the CODEC initialization are as follows:
CODEC Hardware Parameters |
Setting in the |
CODEC |
|---|---|---|
Mic Type |
||
MICBST Mode |
||
SampleRate |
||
I2S Data Format |
||
I2S Channel Len |
||
I2S Data Width |
||
I2S Channel Sequence |
Call
I2S_Cmd()to enable the I2S receive mode. CallGDMA_Cmd()to enable GDMA transfer.
Functional Implementation
After AMIC collects the voice data, the CODEC module AD conversion puts the voice data into the I2S RX FIFO. The data in the I2S RX FIFO is then transferred to the UART TX FIFO via GDMA. In the serial assistant, save the data sent by UART to a file, and parse the file data using audio parsing software. The data transmission order in each module is shown in the figure below.
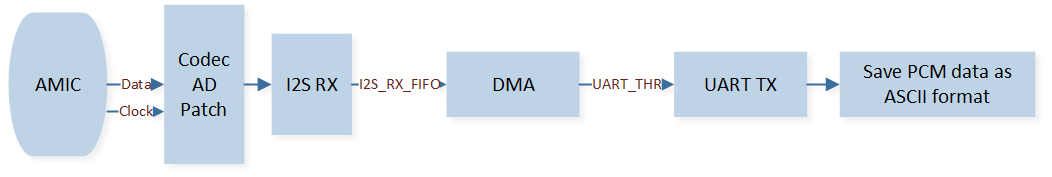
Data Transfer Module (AMIC)
-
When the GDMA transfer amount reaches the set BlockSize, it triggers the
GDMA_INT_Transferinterrupt. As the audio data undergoes AD conversion via CODEC, the data size is relatively large and a single GDMA transfer cannot meet the demand. The source address, destination address, and BlockSize are reset in the interrupt handler, and GDMA transfer is re-enabled to ensure the transmission of a large amount of data continuously.GDMA_SetSourceAddress(GDMA_Channel_AMIC, (uint32_t)(&(I2S0->I2S_RX_FIFO_RD_ADDR))); GDMA_SetDestinationAddress(GDMA_Channel_AMIC, (uint32_t)(&(UART5->UART_RBR_THR))); GDMA_SetBufferSize(GDMA_Channel_AMIC, AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE / 4); GDMA_ClearINTPendingBit(GDMA_Channel_AMIC_NUM, GDMA_INT_Transfer); GDMA_Cmd(GDMA_Channel_AMIC_NUM, ENABLE);
See Also
Please refer to the relevant API Reference: